Explain Modern Theory of Rent With Diagram | Economics
Modern theory of rent is an amplified and modified version of the Ricardian theory of Rent. It was first of all discussed by J.S. Mill and after that developed by economists like Jevons, Pareto, Marshall, Joan Robinson etc.
According to modern theory, economic rent is a surplus that is not peculiar to land alone. It can be a part of the income of labour, capital, entrepreneur.
Explain Modern Theory of Rent
The modern theory of rent is an amplified and modified form of Ricardian theory. This theory was explained by Mrs Robinson Marshall, William Stanley Jevons, etc. According to Modern Economists, rent is a surplus that is not related to land alone, it can be part of the income of labour, capital and entrepreneur also.
According to Modern Economists, “Rent is the difference between actual earning and transfer earning of a factor.”
Rent = Actual Earning – Transfer Earning
Actual Earning: It is that earning which is a factor gets in its present occupation.
Transfer Earning: Transfer earning of a factor is that part of its income which it could get in its next best alternative use. Thus, it is the earning which must be paid to a factor to keep it in its present use.
Why Does Rent Arise?
According to modern theory, the main causes of the emergence of rent are as follows:
-
- Scarcity of Factor: Rent arises due to the scarcity of a factor of production in relation to its demand.
- Specificity of a factor of production: According to Prof. Wiser – there are two types of factors of production:
- Specific factors – Specific factors are those which have no alternative use. The specificity of factors is the main cause of the emergence of rent.
- Non-specific factors – Non-specific factors are those which have alternative uses.
Determination of Rent
According to the modern theory of rent, rent is determined where the demand for factor equals the supply of factor. Modern economists define rent in two ways:
- It is a payment for the use of land only.
- It is a surplus or difference between actual earning and transfers earning.
1. Determination of Rent of Land:
Rent is the payment for the use of land. According to the modern economist, rent arises due to scarcity of land. It is determined by the demand and the supply of land.
- Demand for Land
- Supply of Land
i. Demand for Land
The demand for land is derived from the demand. It means that demand for land depends upon agricultural products, e.g., if the population increases, the demand for food will increase, resulting in increased demand for land and vice-versa. Demand for land is influenced by its marginal productivity. That is why the demand curve DD as shown in fig. slopes downward from left to right.
ii. Supply of Land
The supply of land is fixed for an economy. It is perfectly inelastic; it means its supply is independent of what it earns. Rent is determined at an appointment where the demand curve of land and supply curve of land intersects each other.
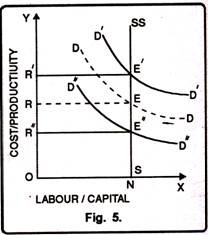
In the figure, DD is the demand curve and SS is the supply curve. E is the point of equilibrium. In this position, OR is rent. If the demand for land increases, the demand curve shifts upwards and becomes D1D1, then the new equilibrium will be E1 and therefore, rent will rise to OR1. If demand decreases DD to D2D2, then the new equilibrium point will be E2 and at this, rent will fall to OR2. Thus, rent is like the price of other goods and is determined by the equilibrium between demand for the supply of land. Rent is paid because of the scarcity of land.
2. Rent as the difference between Actual Earning and Transfer Earning:
According to modern theory, rent arises because there is a difference between actual earning and transfer earning. How much rent a factor of production will get, depending on its elasticity of supply? Supply of a factor can be of three types:
- Perfectly elastic supply
- Perfectly inelastic supply
- Less elastic supply
i. Rent When the Supply of a Factor is Perfectly Elastic
The supply of a factor is perfectly elastic when at the existing rate, supply of the factor can be increased up to any extent. Such a factor is not scary. The actual earning of this factor is equal to transfer earning. Thus, there is no difference between actual earning and transfer earning so rent is zero as shown in the below figure.
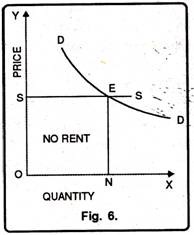
In this figure, units of factors are shown on OX-axis and price is on OY-axis. E is the point of equilibrium and therefore, at OP price, ON units of factor are employed. When demand for factor increases to D1D1, then the new equilibrium point is E1. This equilibrium point shows that when demand for factor increases, its supply also increases. Due to this, the price factor remains the same. In this case, nor rent arises.
Actual Earning = OPE1N1
Transfer Earning = OPE1N1
Actual Earning = Transfer Earning
Rent = OPE1N1 – OPE1N1 = Zero
ii. Rent When the Supply of Factor is Perfectly Inelastic
Supply of a factor of perfectly inelastic when increases or decreases in its demand does not affect its supply. In this case, transfer earning if the factor is zero and whatever the actual earning it gets is called rent as shown in the figure below.
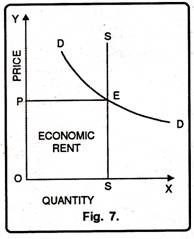
Rent = Actual Earning (Since Transfer Earning is zero)
In this figure, SS is the supply curve and DD is the demand curve of the land. E is the point of equilibrium. At this point, the actual earning of land is OP and transfer earning is zero and rent is OPES. When demand for land increases to D1D1, the actual earning also increase OP to OP1 and transfer earning zero. Thus, the entire earning of this factor is called rent.
iii. Rent When the Supply of Factor is Less Elastic
Supply of a factor is less elastic when increases in its demand id followed by less increase in its supply. Therefore, the actual earning of the factor exceeds its transfer earning which is called rent. It is shown with the help of this figure.
In this figure, SS is a less elastic supply curve and DD is the demand curve. E is the point of equilibrium. At this point, the ON factor is employed at OP price. SS supply curve of factor indicates that the minimum supply price or transfer earning is OS while its actual earning is OP. hence, rent will be PES.
Main Conclusion of Modern Theory of Rent
The main conclusion of the modern theory of rent are as under:
- Rent arises not only to land but all factors of production.
- The rent arises because of scarcity and specificity of factors.
- The amount of rent depends upon the difference between actual earning and transfer earning.
- A factor gets no rent when its supply is perfectly elastic.
- The actual earning of a factor is rent when its supply is perfectly inelastic.
Also Read:
