What are the Principles of Sustainable Development?
Sustainable means that which lasts, continues, or is continued for an extended time. For example, developing a conscious plan of nature-friendly utilization of natural resources and environmental conservation is called sustainable development. Such development works help continue the existence of natural resources and several ecological processes.
The main goal of sustainable development is to balance the population, various resources, various aspects of the environment, and development.
Table of Contents
What is Sustainable Development?
The World Commission on Environment and Development (the Brundtland Commission), in its report to the United Nations in 1987, defined sustainable development as a process in which the direction of investment, the exploitation of resources, and the orientation of technological development and institutional change meet the needs of the current generation without compromising the ability of upcoming generations to meet their needs.
Sustainable development recognizes the mutuality of environmental, social, and economic systems and promotes justice and equality through people empowerment and the wisdom of global citizenship.
Pillars or Aspects of Sustainable Development
Sustainable development emphasizes a positive transformation trajectory anchored essentially on social, economic, and environmental factors. The three main sustainable development issues are economic growth, environmental protection, and social equality.
Based on this, it can be argued that the concept of sustainable development rests, fundamentally on three conceptual pillars. These pillars are “economic sustainability,” “social sustainability,” and ‘environmental sustainability. There has generally been a recognition of three aspects of sustainable development:
- Economic Sustainability
- Environmental Sustainability
- Social Sustainability
1. Economic Sustainability
An economically sustainable system must be able to produce goods and services on a continuing basis, maintain manageable levels of government and external debt, and avoid extreme sectoral imbalances that damage agricultural or industrial production.
2. Environmental Sustainability
An environmentally sustainable system must maintain a stable resource base, avoiding over-exploitation of renewable resource systems or environmental sink functions and depleting non-renewable resources only to the extent that investment is made inadequate substitutes. This includes maintaining biodiversity, atmospheric stability, and other ecosystem functions not ordinarily classed as economic resources.
READ: What is Environmental Scanning? Explain Different Methods of Environmental Scanning.
3. Social Sustainability
A socially sustainable system must achieve distributional equity, adequate provision of social services, including health and education, gender equity, and political accountability and participation.
Clearly, these three elements of sustainability introduce many potential complications to the original simple definition. The goals expressed or implied are multidimensional, raising the issue of how to balance objectives and how to judge success or failure
Relationships Among Environment, Economy, and Social Sustainability
The concept of sustainability appears poised to continue influencing future discourse regarding development science. This implies that the best choices are likely to remain those that meet the needs of society and are environmentally and economically viable, economically and socially equitable, as well as socially and environmentally bearable. This leads to three interconnected spheres or domains of sustainability that describe the relationships among the environmental, economic, and social aspects of sustainable development, as shown in the image below.
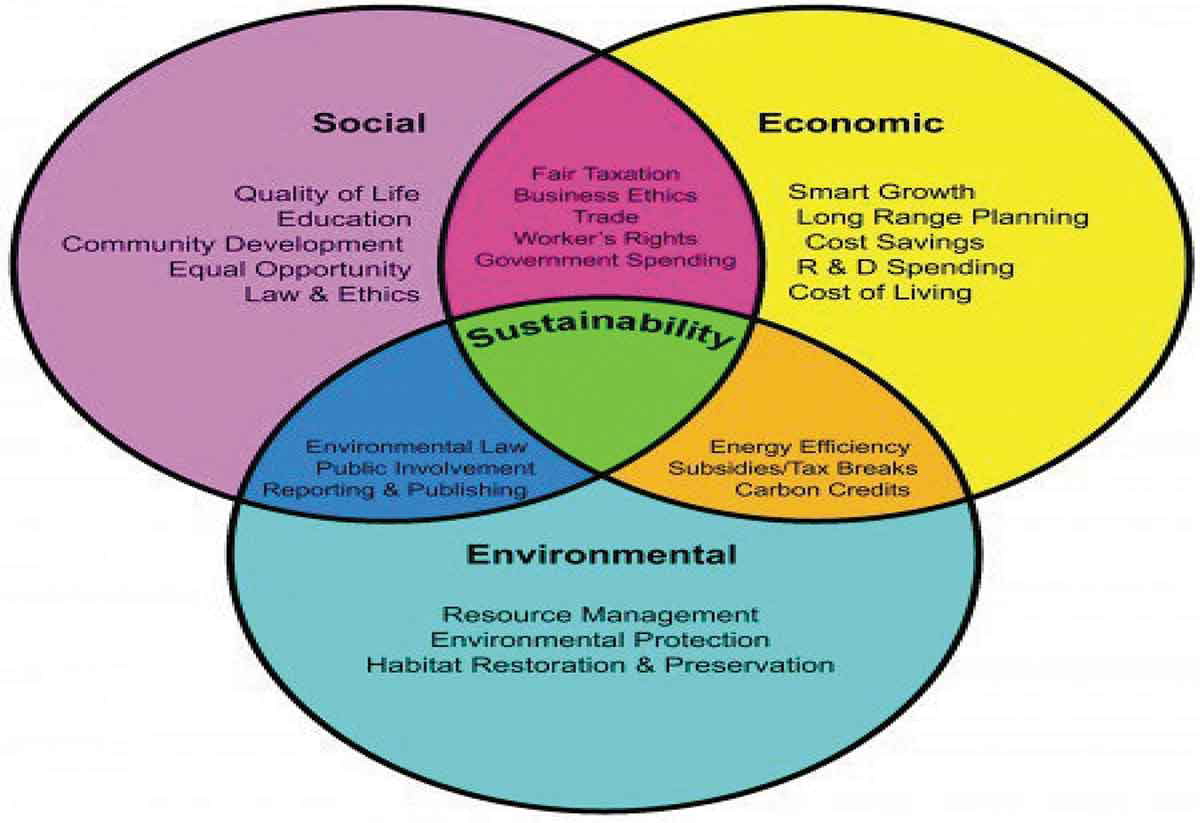
Basically, it can be concluded from the figure that nearly everything man does or plans to do on earth has implications for the environment, economy, or society and the continued existence and well-being of the human race.
What are the Goals of Sustainable Development?
Sustainable development relates to the principle of meeting human development goals while at the same time sustaining the ability of natural systems to provide the natural resources and ecosystem services upon which the economy and society depend. The sustainable development goals primarily seek to achieve the following summarised objectives.
- Eradicate poverty and hunger, guaranteeing a healthy life
- Universalize access to basic services such as water, sanitation, and sustainable energy
- Support the generation of development opportunities through inclusive education and decent work
- Foster innovation and resilient infrastructure, creating communities and cities able to produce and consume sustainably
- Reduce inequality in the world, especially that concerning gender
- Care for environmental integrity through combatting climate change and protecting the oceans and land ecosystems
- Promote collaboration between different social agents to create an environment of peace and ensure responsible consumption and production
Principles of Sustainable Development – Explained in Brief
The principles of sustainable development gravitate towards the economy, environment, and society. Specifically, they relate, among others, to the conservation of ecosystems and biodiversity, production systems, population control, human resource management, conservation of progressive culture, and people’s participation. Some principles of sustainable development are as follows: –
- Conservatoin of Ecosystem
- Sustainable Development of Society
- Conservation of Biodiversity
- Control of Population Growth
- Conservation of Human Resources
- Increase in People’s Participation
- Conservation of Cultural Heritage
- Included Within Carrying Capacity of Earth
1. Conservation of Ecosystem
Sustainable development is passed out with a conservation program for the earth and nature. Natural conservation development mainly includes the conservation of the ecosystem and making it durable. It infers the preservation of natural resources, including biotic factors like birds, animals, plants, etc., and abiotic factors like water, soil, air, etc.
The primary focus of sustainable development is to utilize the components of nature without its over-exploitation and with events of ecosystem conservation. Preservation of terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems is necessary for this purpose.
2. Sustainable Development of Society
Society is comprised of many families and people. Each society needs fundamental aspects like health, education, sanitation, drinking water, tracts, roads, public areas, etc. Using natural components to manage and maintain such aspects in society must be so wise that the natural resources become available for future generations.
With such practice, society can obtain resources for a long time and be sustainable. Moreover, it also helps develop their positive attitude towards nature and living beings.
3. Conservation of Biodiversity
It is essential to conserve all the living beings in the world. The vividness of living creatures should be saved for sustainable development. All living things are integral parts, and people should learn to conserve natural resources to protect living beings.
The decline of any species of living being leaves remarkable effects on the whole ecosystem and harms the environment. Therefore, sustainable development pays keen attention to biodiversity conservation as its main principle.
4. Control of Population Growth
The long-run existence of any development is not possible without a controlled population. Overpopulation increases the total number of consumers, and achievements of development works are overutilized. And the means and resources that are available in the world cannot meet the requirements. Therefore, it affects the positive features of development adversely.
The concept of sustainable development integrates with population control to make it long-lasting. Therefore, population growth control is the main principle of sustainable development.
5. Conservation of Human Resources
Sustainable development is possible with the participation of talented human resources. Skilled and educated human resources are needed for it. They should be qualified for the proper application and implementation of the principles of sustainable development.
Human resources must be developed by providing proper health care, education, and training. Human resources contribute to adopting the principles of sustainable development.
6. Increase in Peoples’ Participation
Sustainable development cannot be sustained personally. Therefore, a joint effort of every individual is indispensable. So, to translate the concept of sustainable development into action, public participation should be increased. Thus, positive public attitudes should be developed in every sustainable development program.
7. Conservation of Cultural heritage
Sustainable development has emphasized the conservation of people’s social traditions, customs, religious places, and cultural aspects. Diverse cultural heritage is a priceless contribution to society, but superstition should be evaded. Conserving the cultural heritage is our responsibility. Its preservation supports sustainable development.
8. Included Within the Carrying Capacity of Earth
Development must be within the carrying capacity of the planet Earth. People cannot instantly get the entire belongings they require from the planet. The world has limited resources, and limited means and resources on the earth cannot be enough for the unlimited means of people. Over-exploitation of the resources has adverse effects on the environment.
17 Principles of Sustainable Development
Many governments and individuals have thought about what sustainable development means beyond a simple one-sentence definition. Development fleshes out the definition by listing 17 principles of sustainability:
Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)

- No Poverty
- Zero Hunger
- Good Health and Well-being
- Quality Education
- Gender Equality
- Clean Water and Sanitation
- Affordable and Clean Energy
- Decent Work and Economic Growth
- Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure
- Reduced Inequalities
- Sustainable Cities and Communities
- Responsible Consumption and Production
- Climate Action
- Life Below Water
- Life on Land
- Peace, Justice, and Strong Institution
- Partnerships For Goals
